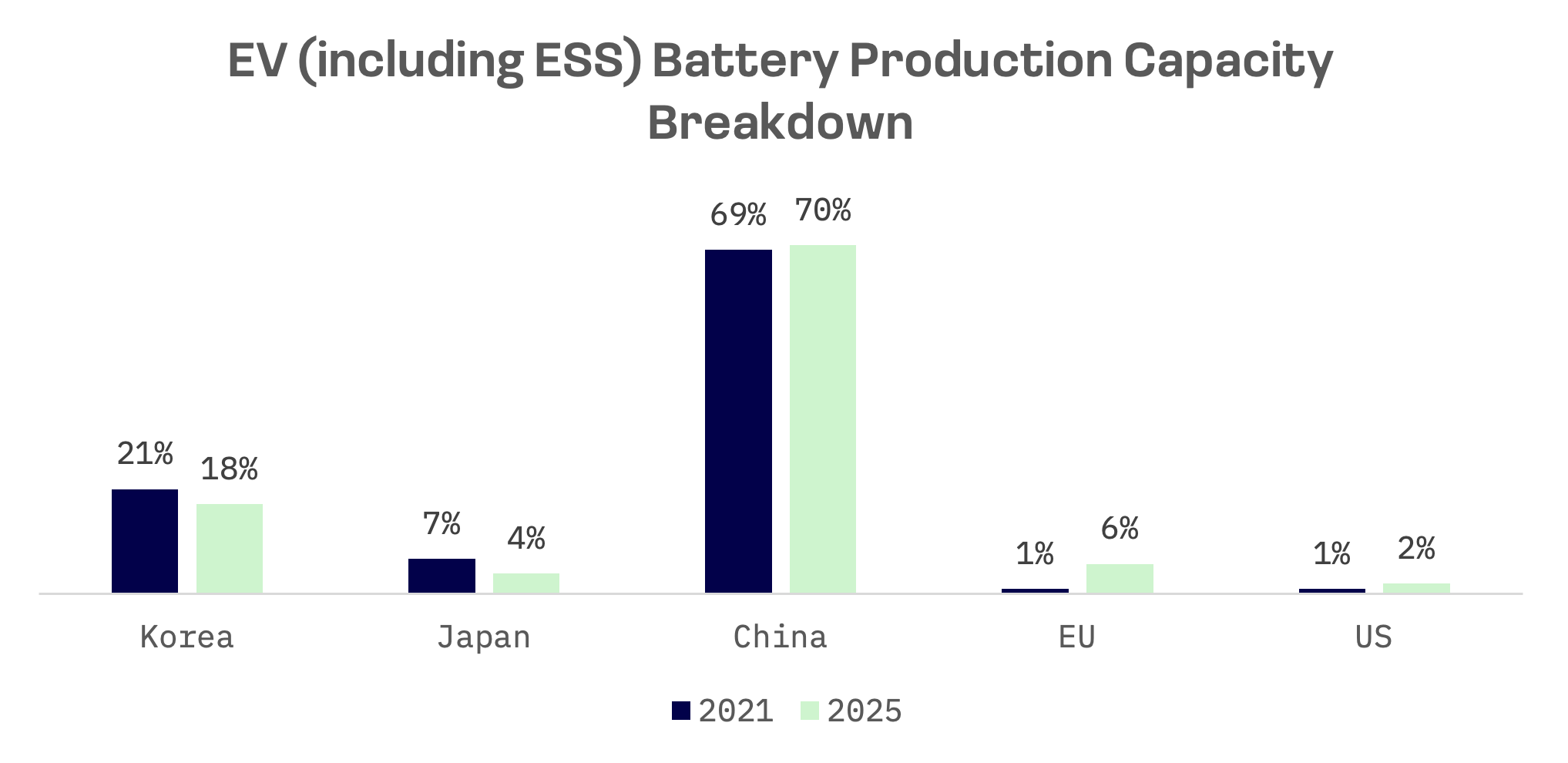
South Korea, the world’s second largest producer of electric vehicle batteries, accounted for 21% of global battery capacity as of 2021, including energy storage systems. The industry has become a linchpin of the Korean economy, ranking as its seventh largest export and employing more than 35,000 workers.
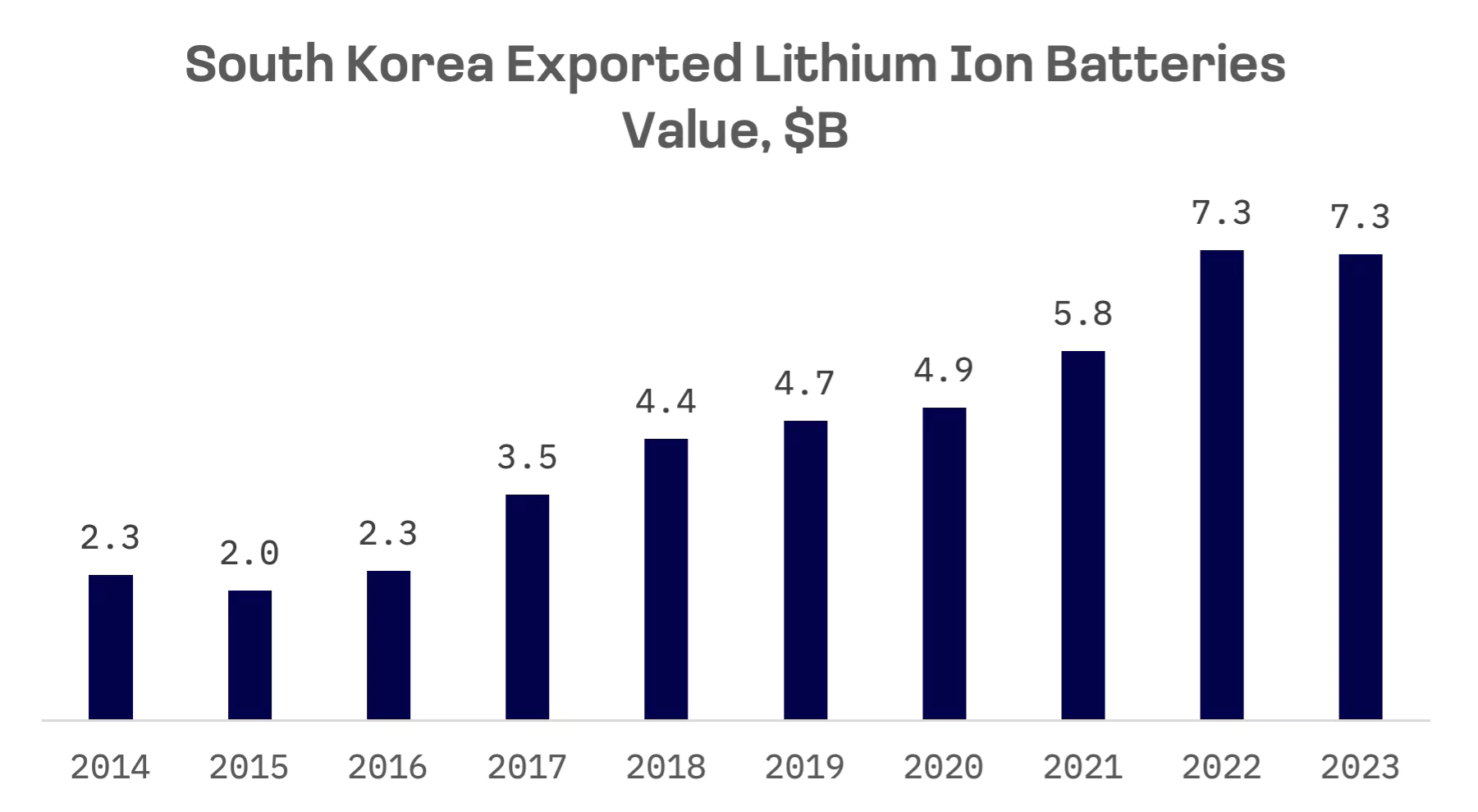
The supply of batteries and battery materials in South Korea has surged exponentially in recent years, alongside a significant increase in exports.
The country is home to manufacturers that are highly competitive on a global scale, both in finished battery products and in critical materials such as anodes and cathodes. LG Energy Solution, Samsung SDI and SK Innovation — collectively known as the “Big Three” of the Korean battery industry — have earned recognition for their competitiveness on the global stage.
LG Energy Solution, a leading global manufacturer of lithium ion batteries, supplies batteries for electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems (ESS) and consumer electronics. As of 2021, it ranks among the top three players in all size segments of the lithium ion battery market.
Samsung SDI, another major player in the global battery market, specializes in lithium ion batteries for EVs and other applications. The company is also involved in the development of solid state batteries.
Sales of Major Global Battery Producers
| Rank | Country | Manufacturer | 2022 EV, GWh | 2022 ESS, GWh |
| 1 | China | CATL | 270 | 53 |
| 2 | Korea | LG Energy Solution | 92 | 9 |
| 3 | China | BYD | 84 | 14 |
| 4 | Japan | Panasonic | 49 | |
| 5 | Korea | Samsung SDI | 36 | 9 |
| 6 | Korea | SK On | 44 | |
| 7 | China | CALB | 24 | |
| 8 | China | Guoxuan | 17 | 6 |
| 9 | China | EVE | 9 | 9 |
| 10 | China | Sunwoda | 11 | |
| OTHERS | 54 | 22 | ||
| TOTAL | 690 | 122 | ||
Source: SNE Research.
This expansion is fuelled by massive investments. According to SNE Research, LG Energy Solution’s EV battery production capacity is set to increase from 173.5 gigawatt-hours (GWh) in 2021 and 505.5 GWh in 2025 to 1,079.5 GWh by 2030. SK On and Samsung SDI have similarly ambitious plans, aiming to reach 233.5 GWh and 156.0 GWh, respectively, by 2025.
Korea’s battery industry is recognized not only for its advanced batteries but also for its strong competitiveness in four critical materials: anode materials, cathode materials, separators and electrolytes. The country produces 25% of the global supply of anode materials, a critical component that accounts for about half of battery costs. Companies like EcoPro BM, LG Chem, Samsung SDI and POSCO Future M are at the forefront of this sector.
All major companies in the Korean battery industry are publicly listed on either KOSPI or KOSDAQ. However, as one of the eight major subsidiaries of SK Innovation, a publicly traded integrated energy and chemical company, SK On is excluded from the table below. This table highlights the four largest companies in the Korean battery industry that are also constituents of the JAKOTA Blue Chip 150 Index.
| Company Name | Ticker | Primary Subsector | Market Cap, USD |
| LG Energy Solution | 373220.KO | EV & ESS Batteries | 82.2B |
| Samsung SDI | 006400.KO | EV & ESS Batteries | 16.1B |
| EcoPro BM | 247540.KQ | Secondary battery materials | 12.9B |
| POSCO Future M | 003670.KO | Secondary battery materials | 12.1B |
Over the past 12 months, all four companies have seen their market capitalization shrink by 30% to 50%, in contrast to the South Korean stock market, where the KOSPI index gained 8%.
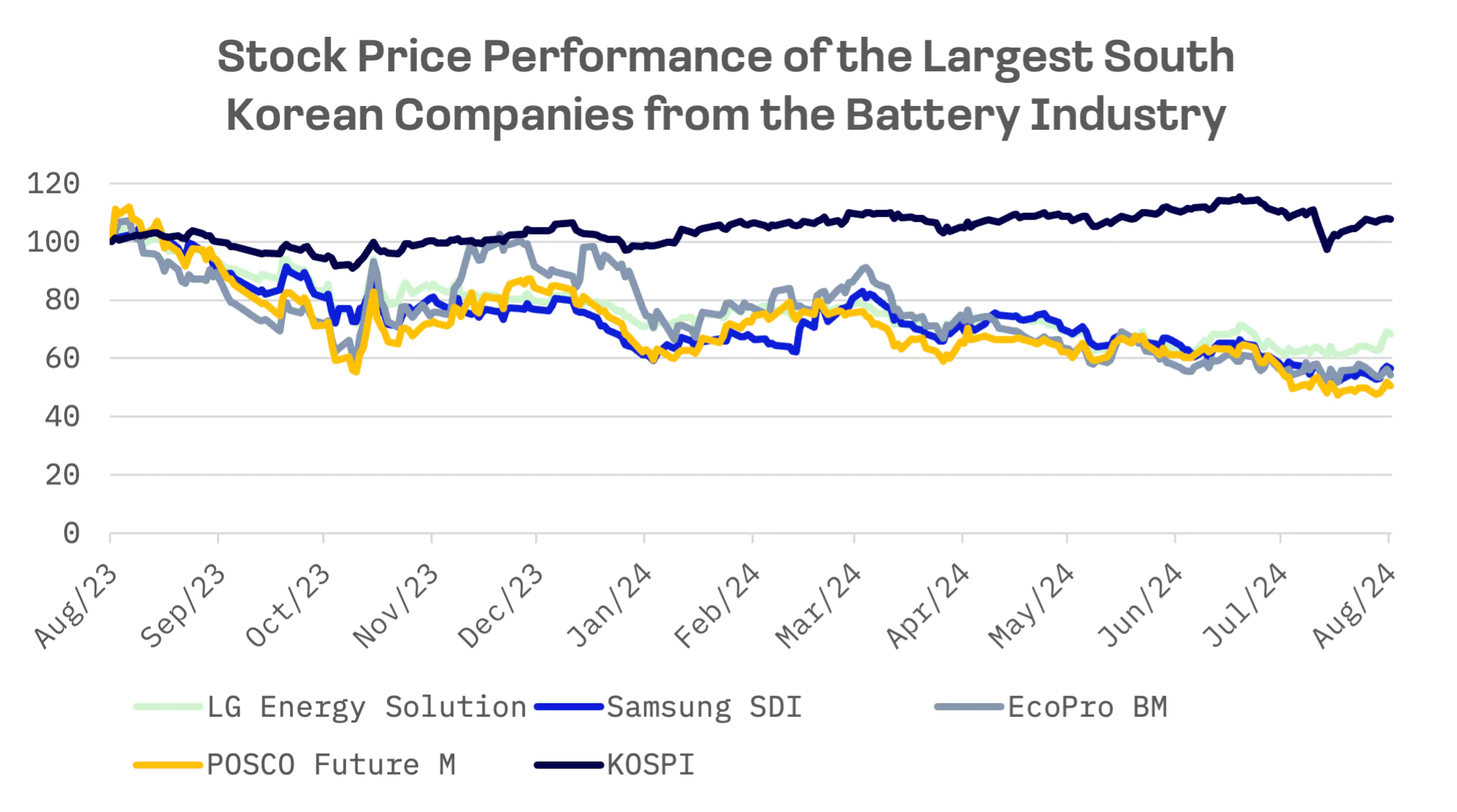
The past year has been challenging for the global EV battery sector. From mid-2023 to early 2024, EV manufacturers experienced declining shipments and increasing inventories. Consequently, annual sales for South Korea’s “Big Three” battery makers are projected to decline by double digit percentages this year compared to last. In contrast, Chinese competitors CATL and BYD are expected to continue growing, as South Korea’s battery sector has struggled to compete with China’s low cost lithium iron phosphate batteries.
Moreover, South Korea depends on China for most of its supply of nickel, lithium and cobalt — the three key minerals that make up half of battery production costs — exacerbating supply chain risks.
Despite these challenges, recent data from SNE Research indicates signs of recovery in global battery shipments and exports since their February 2024 low, driven by the anticipated launch of several affordable EV models in the latter half of the year. Additionally, South Korean companies are adapting to the current environment by producing high quality, price competitive nickel manganese cobalt batteries.
Chinese lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, once viewed as cheaper but inferior alternatives, have made significant technological strides, gaining market share. Meanwhile, Japan’s Panasonic, the pioneer of cylindrical secondary batteries and a key supplier to Tesla in the U.S., is ramping up investment in U.S. production facilities. As a latecomer to the LFP and cylindrical battery markets, South Korea faces the dual challenges of investing in overseas facilities and advanced technologies while grappling with a stagnant domestic market.
Global competition in the battery industry, including U.S. and EU sanctions on foreign battery imports and the intense race to secure raw material supply chains, has exceeded what individual companies can manage on their own. In response, South Korea is taking decisive action. The government plans to allocate ₩38 trillion ($29 billion) over five years to bolster its battery industry. This comprehensive package includes tax incentives and loan support to South Korean firms investing abroad to secure mining rights for essential minerals and other battery materials. It will also enhance financial backing for companies involved in refining and recycling minerals. South Korea also intends to increase financial support through loans, guarantees and insurance from institutions like the Export-Import Bank of Korea, particularly for firms investing in North America to meet the tax allowances stipulated by the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
LG Energy Solution, the market leader, is weathering the storm better than its peers. The company is leveraging joint ventures and localized production to maintain its edge. By pooling resources and increasing production volumes, LG Energy Solution’s joint ventures can achieve economies of scale, thus reducing per unit costs. For instance, its ventures in Indonesia benefit from local raw material availability and lower operational costs, while those in U.S. capitalize on advantages provided by the IRA.
The Ultium Cells 2 plant in Tennessee, a joint venture between LG Energy Solution and General Motors, began full operations in March with a ₩2.7 trillion investment. This plant is set to supply batteries for GM’s next generation EVs, using high energy density nickel cobalt manganese aluminum pouch type batteries. It aims to expand its production capacity to 50 GWh, sufficient to power approximately 600,000 high performance EVs with a range exceeding 500 km.
In the second quarter of this year, LG Energy Solution secured a record ₩1.31 trillion in IRA tax credits, representing 52.2% of its ₩2.51 trillion cumulative operating income from the past six quarters. Despite these incentives, the company’s second quarter revenue fell to ₩6.16 trillion, with operating profit dropping to ₩499.32 billion, down 45.5% from the previous year.
LG Energy Solution Key Financial Indicators
| Fiscal Q2 2024 ended 6/30/24, KRW | YoY, % | |
| Revenue | 6.16T | -29.77% |
| Operating expense | 945.37B | -3.96% |
| Net income | -471.77B | -209.09% |
| Net profit margin | -7.66% | -255.38% |
| Earnings per share | -2.02K | -209.09% |
| EBITDA | 499.32B | -45.52% |
To maximize the utilization rate at each production site, LG Energy Solution is also exploring the conversion of existing battery production lines for applications such as ESS and new products.
Despite facing challenges, South Korea is emerging as a major player in the global battery industry. The country’s substantial role in supplying cathode materials positions it favorably to become a key battery hub. Moreover, the presence of leading battery manufacturers in the country fosters strong partnerships and joint ventures through strategic collaborations, enhancing its global influence in the industry.



